Work, Energy and Power
Work, Energy and Power: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Units of Work and Definition of Joule, Law of Conservation of Energy, Units of Energy & Average Power etc.
Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
When a body moves with a constant speed along a circle
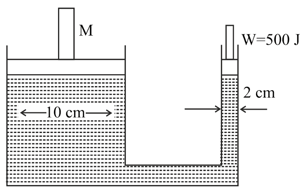
The hydraulic press given in the figure is used to raise the mass M through a height of by performing of work at the small piston. The diameter of the large piston is , while that of the smaller one is . The mass M is:
Which energy does not convert into work done completely.
The rate of work done is called
If speed of a car becomes times, its kinetic energy becomes
What is the SI unit of work?
What is the CGS unit of work?
The work done to increase the velocity of a car from to , if the mass of the car is , is:
Which of the following graphs shows correct relation of kinetic energy (E), potential Energy (U) and height (h) from the ground of a particle?
Spring constant of a spring is . Work done to stretch it from mean position is
How fast should a man weighing run to achieve a kinetic energy of . Take .
A person of mass reaches a height in . Find the power used by the person ().
Which of the following graphs best represent the graphical relationship between Kinetic Energy and momentum of a body in motion?
Heat and work done by the heat was discovered by
In a simple Pendulum the displacement is equal to amplitude. Then kinetic energy will be
The temperature of the water at the bottom of a water fall is higher than that of the water at the top, because :
A rod of length and mass fixed at one end, is hanging vertically. The other end is now raised so that the rod makes an angle with horizontal line. The work done in the process will be :
A force of acts on a body, and body moves through a distance of metre at an angle of in the direction of the force. The work done by the force is
